Python Tutorials
Basic
Data Structure and Data Types
String
List
Tuple
Set
Dictionary
Functions / Methods
Advance
Exception Handling
Python Types Of Inheritance
Types Of Inheritance
Python inheritance helps to reuse the code of existing classes.
We can classify inheritance in Python based on how many child classes there are and the pattern of inheritance.
- Single Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance
Single Inheritance
A single inheritance involves only two classes, where one class inherits another.
It is the simplest type of inheritance, where a single child class inherits the properties and functions of a parent class.

Single inheritance represents an "IS A" relationship. Example:- Rose is a flower. (A flower represents class A, and a rose represents class B.)
Example
class A:
def function_a(self):
print("Function call from class A.")
class B(A):
def function_b(self):
self.function_a()
print("Function call from class B.")
obj = B()
obj.function_b()
Function call from class A.
Function call from class B.
In the above example, we are inheriting class A in class B and accessing the class A function (function_a()) in class B using self.
Multilevel Inheritance
In multilevel inheritance, more than two classes are involved; the child class inherits another child class.
A chain of inheritance in which a parent class is a child of another class.

Multilevel inheritance represents "IS A" relationships at multiple levels. Example:- A Rose is a flower, and a flower is a plant. (The plant, flower, and rose represents classes A, B, and C respectively.)
Example
class A:
def function_a(self):
print("Function call from class A.")
class B(A):
def function_b(self):
self.function_a()
print("Function call from class B.")
class C(B):
def function_c(self):
self.function_b()
print("Function call from class C.")
obj = C()
obj.function_c()
Function call from class A.
Function call from class B.
Function call from class C.
Here, we are inheriting class A in class B and class B in class C.
In this case, class A is the parent class for B, and B is the parent class for class C.
Multiple Inheritance
Multiple inheritance occurs when one class inherits several other classes.
It allows the child class to access all the methods and properties of its parent classes.

Example
class A:
def function_a(self):
print("Function call from class A.")
class B:
def function_b(self):
print("Function call from class B.")
class C(A, B):
def function_c(self):
self.function_a()
self.function_b()
print("Function call from class C.")
obj = C()
obj.function_c()
Function call from class A.
Function call from class B.
Function call from class C.
In the above example, we are inheriting classes A and B in class C.
Hierarchical Inheritance
In hierarchical inheritance, multiple classes inherit a single-parent class.

Using hierarchical inheritance is useful when multiple classes have an "IS A" relationship with a single-parent class. Example:- A rose is a flower, and a lily is also a flower. (Class A is a flower, while classes B and C are rose and lily.)
Example
class A:
def function_a(self):
print("Function call from class A.")
class B(A):
def function_b(self):
self.function_a()
print("Function call from class B.")
class C(A):
def function_c(self):
self.function_a()
print("Function call from class C.")
obj_b = B()
obj_b.function_b()
obj_c = C()
obj_c.function_c()
Function call from class A.
Function call from class B.
Function call from class A.
Function call from class C.
Here, we are inheriting the class A with the classes B and C.
Hybrid Inheritance
In Python, hybrid inheritance refers to combining more than one type of inheritance.
Hybrid inheritance is not a sequence or pattern of inheriting classes but rather a naming convention used for more than one type of inheritance.

Example
class A:
def function_a(self):
print("Function call from class A.")
class B(A):
def function_b(self):
self.function_a()
print("Function call from class B.")
class C(B):
def function_c(self):
self.function_b()
print("Function call from class C.")
class D(B):
def function_d(self):
self.function_b()
print("Function call from class D.")
obj_c = C()
obj_c.function_c()
obj_d = D()
obj_d.function_d()
Function call from class A.
Function call from class B.
Function call from class C.
Function call from class A.
Function call from class B.
Function call from class D.
In the above example, we combined the multilevel and single inheritance.
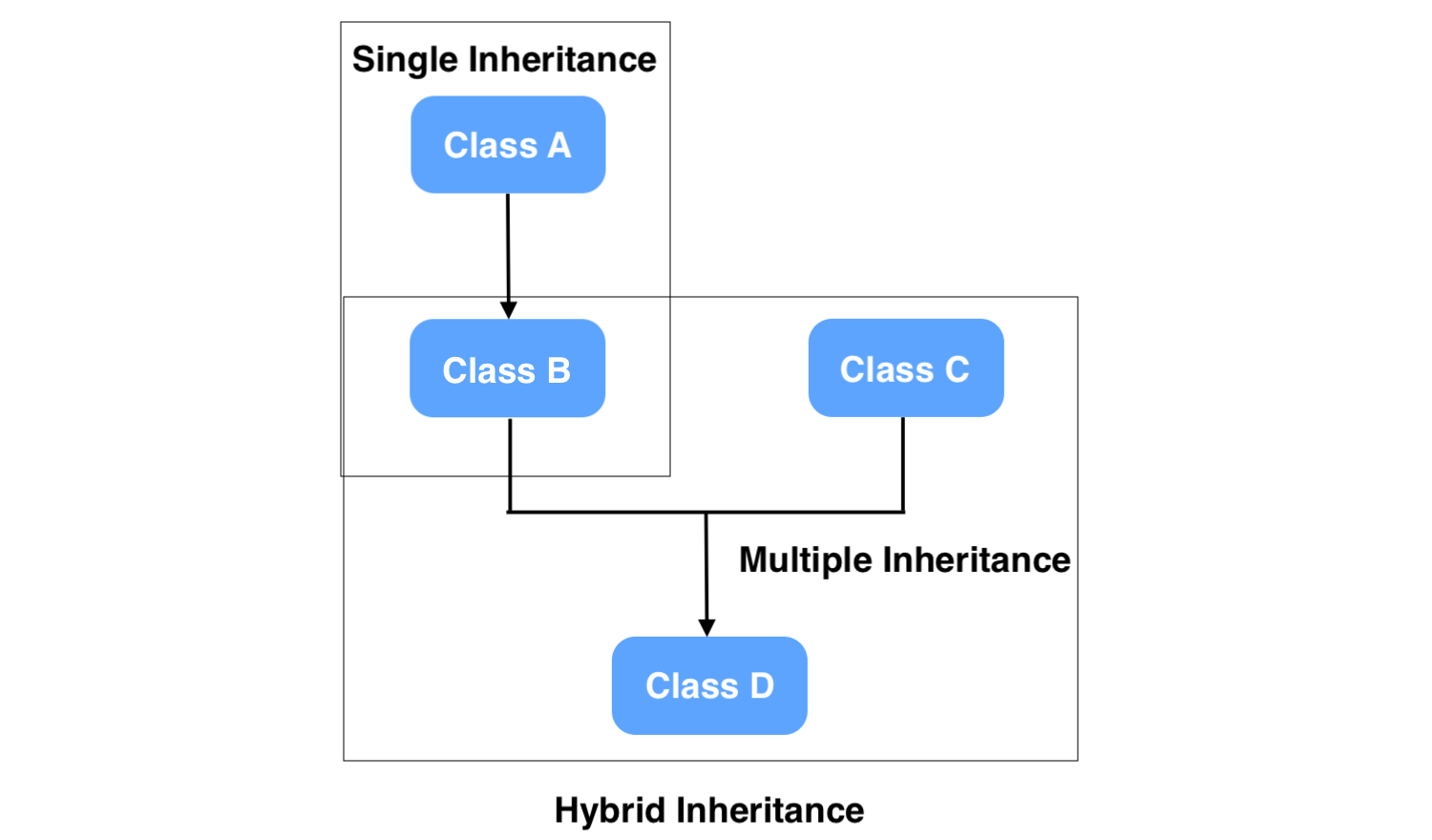
Example
class A:
def function_a(self):
print("Function call from class A.")
class B(A):
def function_b(self):
self.function_a()
print("Function call from class B.")
class C:
def function_c(self):
print("Function call from class C.")
class D(B, C):
def function_d(self):
self.function_b()
self.function_c()
print("Function call from class D.")
obj_b = B()
obj_b.function_b()
obj_d = D()
obj_d.function_d()
Function call from class A.
Function call from class B.
Function call from class A.
Function call from class B.
Function call from class C.
Function call from class D.
In the above example, we combined the multiple and single inheritance.